With BlueConduit’s new LSL Replacements tool coming online, we’ve been talking a lot about data clustering or grouping. BlueConduit CEO Lorne Groe even called out data clustering as the functionality he’s most excited about in the new tool.
So what is data clustering and why is it important for LSL replacements? Let’s dig in.
What is data clustering?
A service line inventory identifies service line materials for every address, one-by-one. This is critical data for understanding the volume of lead service lines in a water system and for understanding where, exactly, you will need to dig to replace all of your lead service lines.
But this line-level data is much less helpful when it comes to LSL replacement planning. Why? Large infrastructure projects are not planned around address-level geographies. Rather, they are planned by larger chunks of work that can be allocated to a city crew or contractor. These larger geographies could be a street, a cluster of streets, or maybe a neighborhood.
Data clustering, as it relates to LSL replacement planning, means aggregating service line material data to a larger geography, such as a street-level, for the purposes of planning.
Why is data clustering so important for LSL replacement planning?
When it comes to LSL replacements, order matters. Since utilities are likely to have limited funding for replacements, they must make critical decisions about what lines need to be replaced right away and what lines can wait.
Data and data clustering enables this optimization in replacement planning. When data is clustered to street-level, it can be prioritized by those street-level clusters (same is true for other location groupings).
Let’s assume a water system wants to consider 4 main factors when prioritizing LSLs for replacement – presence of children, proximity to schools, income levels, and zoning to prioritize residences, with presence of children weighted most strongly in the prioritization.
With data clustering, the water system can generate a ranked priority list at a street or block level view, rather than a service line view. This view enables the water system to then make replacement prioritization decisions that maximize resources while reducing neighborhood disruption.
How does BlueConduit’s software manage data clustering?
BlueConduit’s LSL Replacements software visualizes service line inventory data alongside other critical datasets including the U.S. Census Bureau’s Presence of Children, Environmental Justice Index, demographic factors, and proximity to key locations. The software then allows the utility to view these results beyond the parcel level to a street or block view.
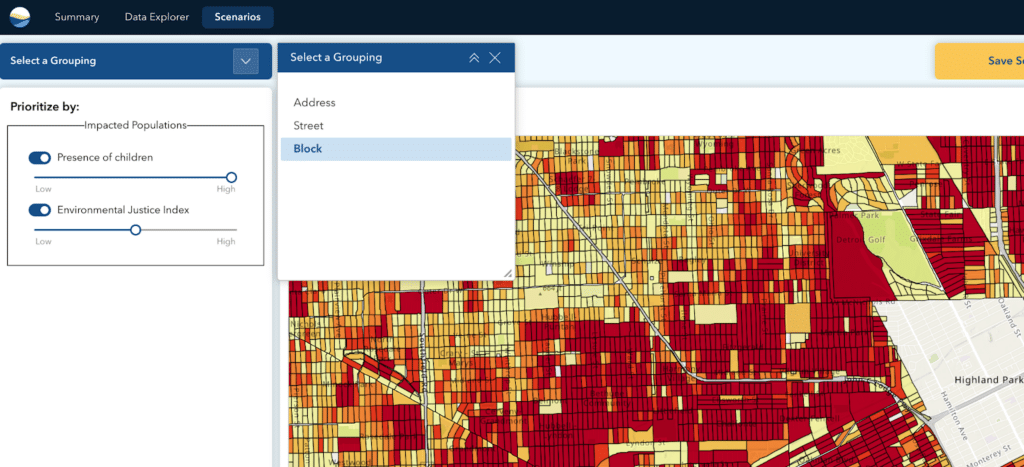
Within the selected view, users can utilize Prioritization tools that generate a priority score based on the specific combination of weighted factors selected. Prioritization selections can be further refined as users explore real-time indicators showing the impact of their decisions. Based on prioritization decisions, users can then select locations manually and using smart recommendations and filters, to identify the specific clustered locations where replacement should begin. Integrations into a water system’s asset management tools enable alignment with existing infrastructure project schedules as well as batched, automated creation of work orders.
LSL replacement planning is messy and complex. BlueConduit’s new LSL Replacements tool streamlines planning and supports water system leaders and enables them to do what they do best – make high quality decisions that are right for their community.
Want to learn more about BlueConduit tools and support for LSL replacement? Schedule a consultation today.